TOPIC 1: PROCESS COMPUTERIZED DOCUMENT
(Outline Notes)
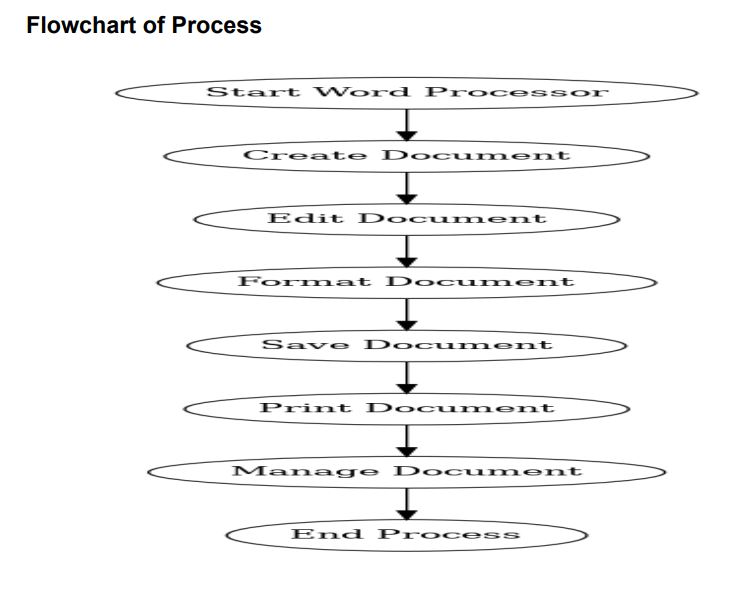
Start Word Processor – open MS Word / Google Docs / LibreOffice.
Create Document – type text, apply basic formatting (fonts, size, bold, italics).
Edit Document – cut, copy, paste, delete, spell & grammar check.
Format Document – page setup, alignment, line spacing, tables, images, styles.
Save Document – use proper filename, file format (.docx, .pdf), save often.
Print Document – preview, adjust settings, print or export as PDF.
Manage Document – organize (rename, move, copy), share, secure with password.
The process covers creation → editing → formatting → saving → printing → managing documents with word processing software.
- Starting the Word Processor
-
Launch the word processing software (e.g., MS Word, Google Docs, LibreOffice Writer).
-
Open a new or existing document.
-
-
Creating a Document
-
Enter text using the keyboard.
-
Use formatting tools (font style, size, bold, italics, underline).
-
Insert page elements (headings, paragraphs, bullets, numbering).
-
-
Editing the Document
-
Modify text: cut, copy, paste, delete, or replace.
-
Use spell check and grammar check for accuracy.
-
Rearrange or restructure content as required.
-
4. Formatting the Document
-
-
Adjust page layout (margins, orientation, size).
-
Apply styles to headings, subheadings, and body text.
-
Insert tables, images, charts, or symbols.
-
Use alignment, line spacing, and indentation for clarity.
-
5. Saving the Document
-
-
Save the file with a proper name and location.
-
Choose appropriate file format (e.g., .docx, .pdf, .rtf).
-
Save regularly to prevent data loss.
-
6. Printing the Document
-
-
Preview before printing.
-
Adjust print settings (page range, copies, orientation).
-
Send document to printer or export as PDF.
-
7. Managing the Document
-
-
Rename, move, or copy files for organization.
-
Share via email, cloud storage, or external devices.
-
Apply security features (password protection, restricted editing).
-
Ergonomics Risk Factors
Ergonomics is the science of designing the workplace, tools, and tasks to fit the worker,
reducing strain and promoting efficiency. Poor ergonomics can lead to musculoskeletal
disorders (MSDs), fatigue, and reduced productivity.
Common Ergonomic Risk Factors:
1. Repetition – Performing the same motion repeatedly (e.g., constant typing or clicking)
increases the risk of strain injuries like carpal tunnel syndrome.
2. Awkward Postures – Working with the body in unnatural positions (e.g., bending wrists,
slouching, or twisting the neck) puts stress on muscles and joints.
✅ Prevention: Adjust workstations, take breaks, use ergonomic furniture, and maintain good
posture.
3. Forceful Exertions – Applying high physical effort (e.g., heavy lifting, forceful
gripping) can cause injuries.
4. Contact Stress – Continuous pressure from hard edges (e.g., desk edges pressing against
wrists) leads to discomfort and circulation problems.
5. Static Postures – Staying in one position for too long (e.g., sitting without breaks)
reduces blood circulation and increases fatigue.
6. Environmental Factors – Poor lighting, excessive noise, high temperatures, or vibration
from machines can strain the body and mind.
7. Improper Workstation Setup – Wrong desk/chair height, poorly positioned monitor, or
non-ergonomic keyboard/mouse can contribute to health risks
1.2 Creation of Computerized Word
Document
1.2.1 Introduction to Word Document
A word document is a computerized file created using a word processing software to prepare,
edit, format, and store text-based information. Unlike typewriters, word processors allow easy
corrections, text formatting, and integration of multimedia.
- Features of Word Documents:
Text entry and editing
Formatting (fonts, styles, alignment, spacing)
Insertion of tables, charts, and images
Spell-check and grammar tools
Saving, printing, and sharing documents electronically
✅ Importance: Used in offices, schools, and organizations for reports, letters, assignments, and
professional documents.